Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
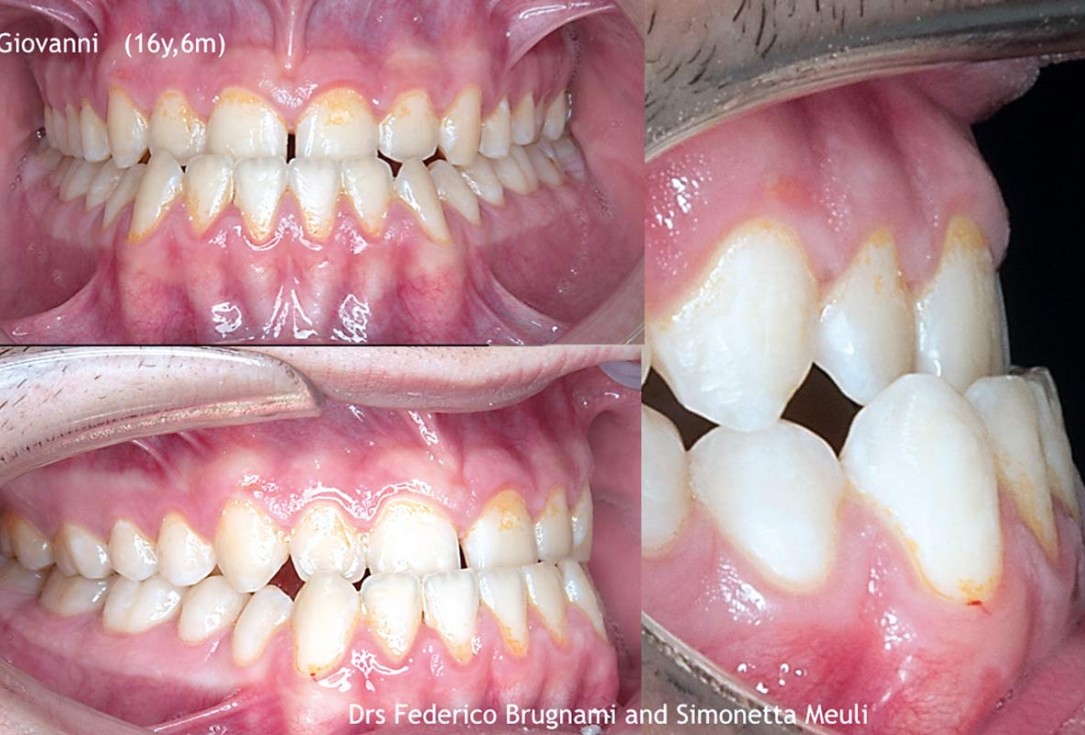
1/12 - Initial view of the clinical case: Class III malocclusion Treatment plan: Regenerative corticotomy (PAOO)Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
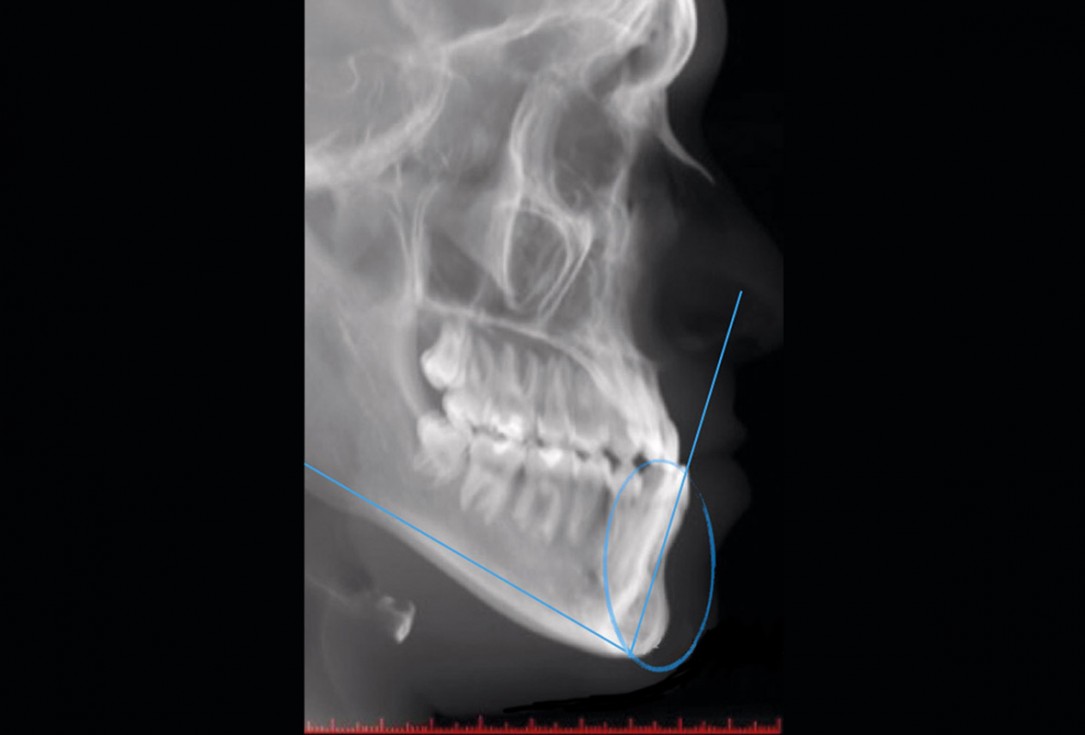
2/12 - Pre-op x-ray reveals skeletal class III.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
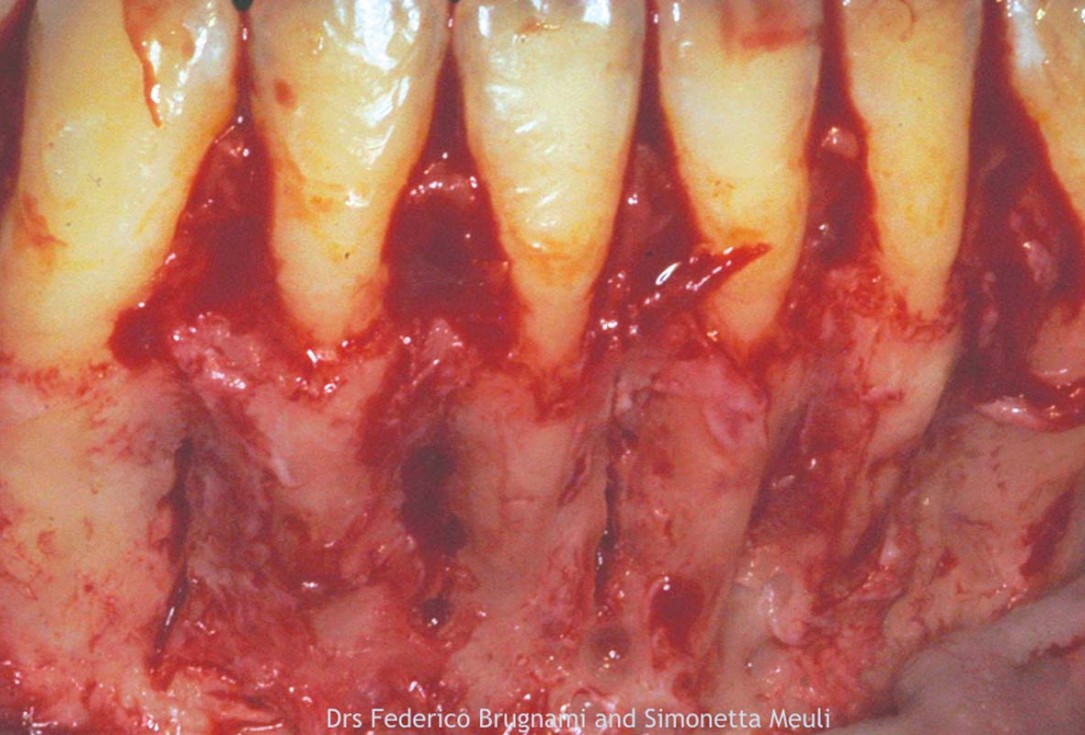
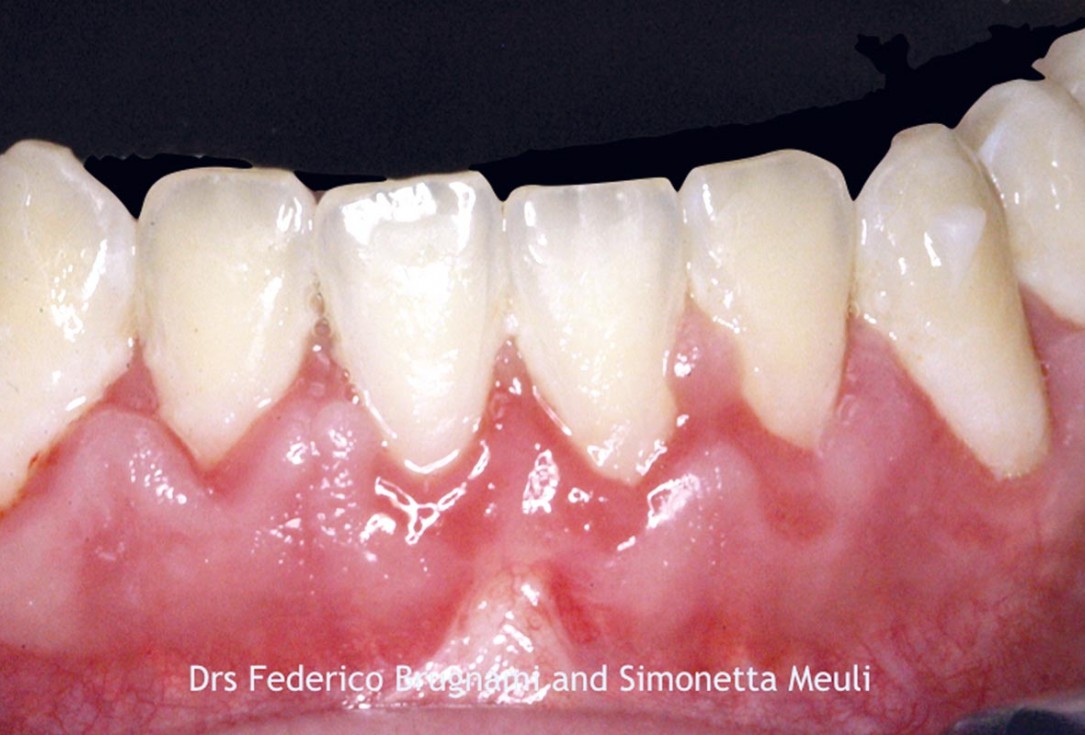
3/12 - Dehiscence defect and thin buccal plate.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
4/12 - PAOO protocol includes a surgical preperation of the cortical bone which can be performed with rotary instruments or piezo-electric scalpels.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
5/12 - A layer of cerabone® applied -as reliable and volume stable bone substitute.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
6/12 - mucoderm® acting as a barrier membrane and as a soft tissue graft. The combination of hard and soft tissue grafting increases the bone regeneration and the soft tissue thickness. Thus, enhancing the clinical outcome.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
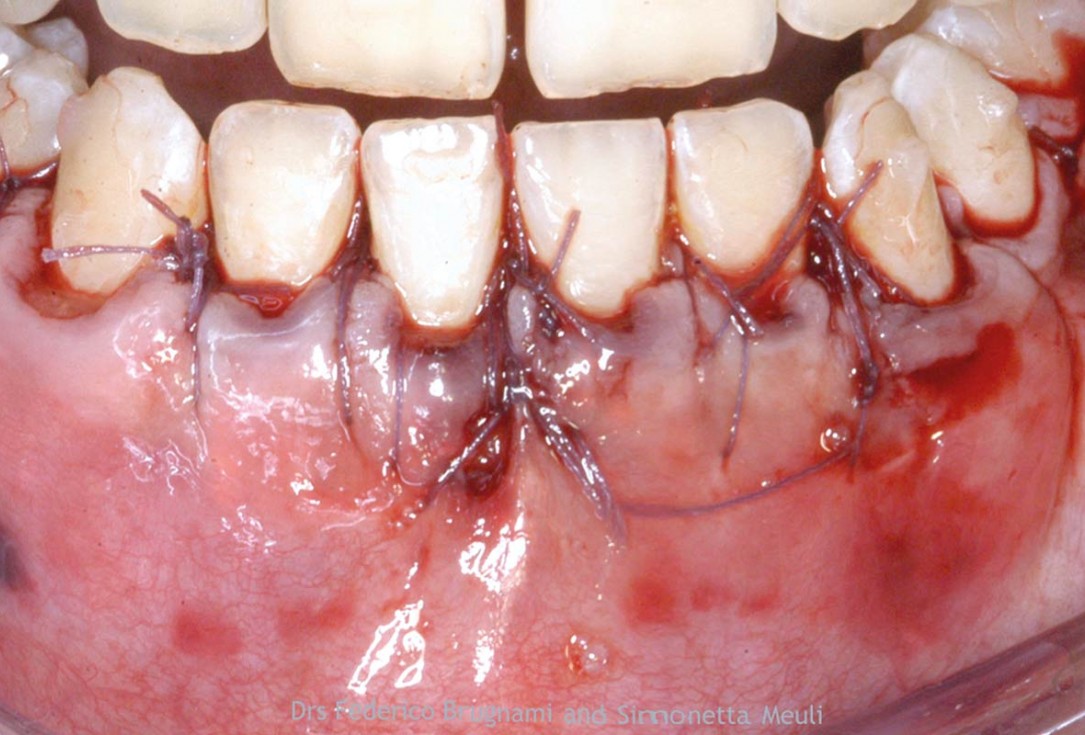
7/12 - Primary closure of the area is ensured by coronally positioning the flap. Mobilization of the flap is obtained undermining the periostium at the base of the flap.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
8/12 - Two weeks post-op showing excellent augmentation of the area and some minor marginal gingival inflammation.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
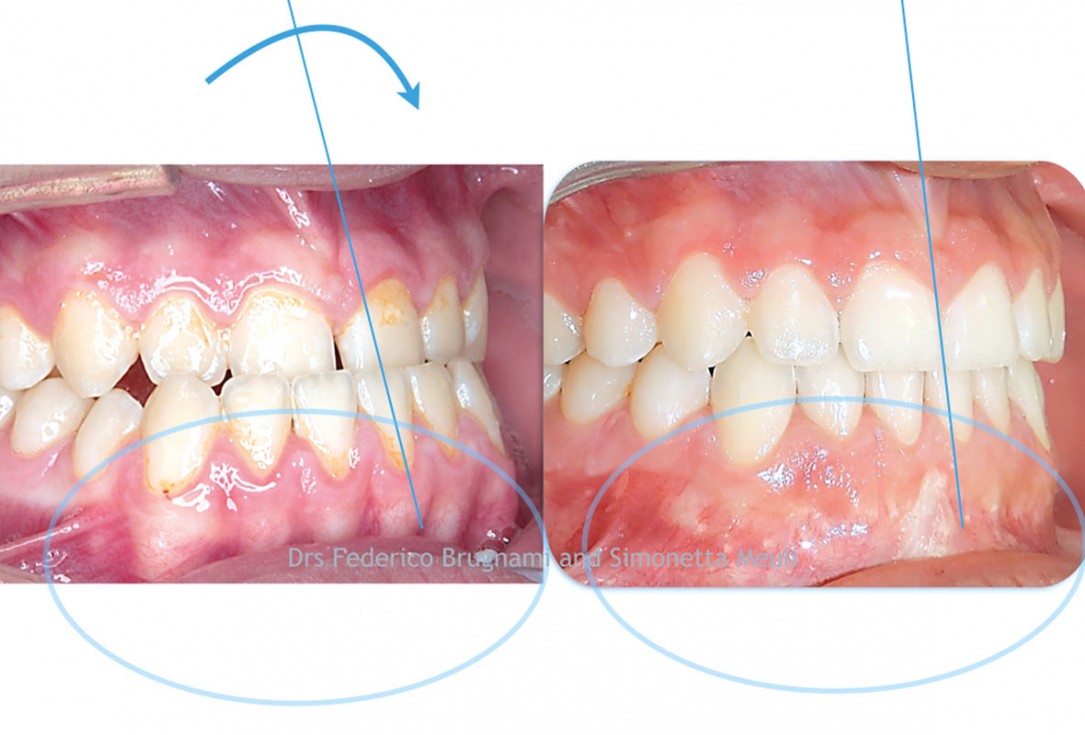
9/12 - Frontal view: Before and after orthodontics, orthognatic surgery and periodontal therapy with the regenerative corticotomy. Repaired recessions and increased thickness of gingiva.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
10/12 - Lateral pre-op and post-op view: Evident change in position of the incisors and the augmented vestibular periodontium.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
11/12 - Pre and post-op x-ray reveals counter-clock rotation of the mandibula due to the orthognatic surgery and the vestibular inclination of the incisors due to the orthodontic treatment.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli
-
12/12 - Pre and post-op CT showing a great bone volume gain in the lower frontal area. Confirming the augmentation of not only the soft tissue, but also of the hard tissue components.Regenerative corticotomy to compensate lower incisor malocclusion with cerabone® and mucoderm® - Dr. F. Brugnami & Dr. S. Meuli

Extraction of tooth 44

Pre-surgical clinical situation. Multiple adjacent gingival recessions at teeth 12,13 and 14.

Initial clinical situation. Multiple adjacent gingival recessions in regio 11-13.

Pre-operative clinical situation. Gingival recession at the first premolar.

Insufficient keratinized mucosa and extremely shallow vestibule on the maxilla

Initial clinical situation

Initial clinical situation

Initial clinical situation with lack of keratinized tissue

Lack of sufficient keratinized mucosa following extensive horizontal ridge augmentation

Pre-operative clinical situation. Multiple adjacent gingival recessions.

Longitudinal fracture on the root resected tooth 21 with visible buccal fistula

Tooth extraction due to root fracture

Drilling template for guided implant placement

Clinical situation before extraction

Initial situation: missing teeth #11 & 12 and badly broken #21 root

Initial clinical situation with Miller class 1 recession

Initial view of the case. Discoloration of 1.1 and mild class I gingival recession

Preoperative situation – Maxillary defect in area 14-16 (loss of implant 16 due to periimplantitis, tooth 14 extracted recently and area 15 already edentulous for a while)

Initial clinical situation shows an odontogenic fibroma that was growing for years

Initial clinical situation with pronounced vertical and horizontal bone defect

Initial clinical situation - Central incisors with dental destruction and periapical pathology

Situation before extraction of the teeth

Multiple adjacent gingival recessions.

Pre-surgical situation. Multiple adjacent gingival recessions at teeth 12, 13 and 14.

Pre-operative clinical view. Multiple adjacent gingival recessions.

Initial clinical situation with narrow ridge

Pre-operative clinical situation. Gingival recessions at teeth 11 and 21.

Initial clinical situation

X-ray shows a 3-dimensional periondontal defect

Clinical situation before surgery

Baseline clinical situation, frontal view.

X-ray showing endodontic failure of the molar

Initial clinical situation showing severe soft tissue loss

Alveolar socket before soft and hard tissue augmentation

Clinical situation

Initial clinical situation showing strongly compromised tooth 21

Initial view of the clinical case: Class III malocclusion
Treatment plan: Regenerative corticotomy (PAOO)

Initial clinical view of the case. Soft tissue dehiscence around implants 26.

Initial situation displaying insufficient bone width

Occlusal view of attached maxgraft® cortico at the buccal site

Initial situation before surgery. Patient lost central incisors 1 month ago due to endodontic failures

Initial clinical situation

Gingival recession at tooth 13. Free gingival graft (FGG) of a previous surgery for root coverage visible.

Initial clinical situation

Pre-surgical clinical situation. Deep gingival recessions at both upper canine.

Initial clinical situation with traumatic loss of tooth 21

Pre-operative clinical situation. Shallow multiple adjacent gingival recessions in the first quadrant.

Initial clinical situation

X-ray of initial clinical situation

Multiple adjacent recessions in the upper jaw.

recession on tooth 11

Full-thickness flap preparation bucally and lingually

Intact socket following atraumatic tooth extraction

X-ray control before tooth extraction

Bone defect in area 11-21 due to two lost implants (periimplantitis) after 15 years of function

Pre-operative clinical situation: changed color in the gingiva in the front maxilla

Initial clinical situation showing tooth 45 not worth preserving

Initial situation - A young female 34 years old lost her front teeth in an surfing accident and she had a 5 unit bridge supported by her upper left lateral and right canine. The restoration failed and both supporting crowns have exposed and leaking margins.

Clinical view 8 weeks after extraction of teeth 25 and 26