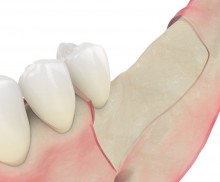
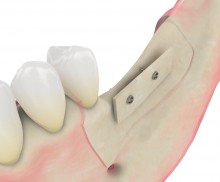
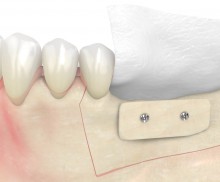
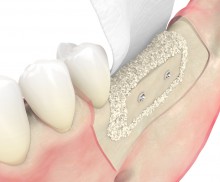
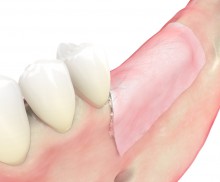
Shell technique
|

A microsaw is typically used to harvest a bone block, which is then split into two to three thin bone plates. The thickness of these bone plates can be further reduced with a safescraper or a bone mill. The harvesting process, although ensuring excellent results, presents several issues, i.e., it is time consuming, may causes more discomfort to the patient than the augmentation itself, and is a possible source of complications.
As an alternative to the harvesting of autologous bone, maxgraft® cortico is an excellent option: Its natural origin (e.g., the human bone) ensures a high osteoconductivity, controlled remodeling, and biomechanical properties, making maxgraft® cortico the material of choice for bone augmentation; maxgraft® cortico is a sterile product (e.g., no antigenicity) with a high stability and a shelf life of 5 years.
After plate fixation, the space between local bone and cortical plate can be filled with a variety of different particulate bone grafting materials. To facilitate osteosynthesis, allogenic particles (e.g., maxgraft® granules) can be used to fill the defect. The preserved human collagen provides an excellent osteoconductivity and enables a complete remodeling. Mixing with autologous chips or particulate PRF matrices can also support the ossification. At the end of the procedure, the augmentation area is covered with a barrier membrane (e.g., Jason® membrane); a tension-free and saliva-proof closure is finally applied.
Please Contact us for Literature.